PENYELIDIKAN
SAINS TERNAKAN
Scope of Research
- Conduct research in the field of livestock science
- Develop technologies, products, and knowledge in the field of livestock science.
- Function as a reference centre for livestock science
Expertise
- Breed Development Programme
- Animal breeding and genetics
- Livestock reproduction
- Animal modelling and simulation
- Beef production
- Poultry production
- Small ruminant production
- Advanced & Reproductive Technologies Programme
- Reproductive Biotechnology
- Semen collection and processing
- Artificial Insemination
- Embryo production and transfer
- Animal Tissue Culture
- Molecular Biology
- Genetic Characterization using DNA markers.
- Genetic Characterization using DNA markers.
- Reproductive Biotechnology
- Production System Programme
- Ruminant production system
- Non-ruminant production system
- Pasture and fodder production system
- Meat Science
- Dairy Science
- Livestock economics
- Feed & Nutrition Programme
- Feed chemistry and biochemistry
- Nutrient digestibility and metabolism (in vitro, in vivo, in sacco)
- Feed formulation and feeding strategies for livestock.
- Microbiology and feed safety
- Animal feed processing and bioprocessing techniques
Teknologi
Lembu KK Elit ialah baka tempatan yang sesuai untuk penternakan, dengan pejantan matang 430 - 460 kg dan induk betina 220 - 250 kg pada usia 3 - 4 tahun. Ia tahan terhadap parasit, beradaptasi dengan iklim Malaysia, dan memiliki prestasi pembiakan yang baik (kadar kebuntingan 80 - 90%). Lembu ini dapat menghasilkan karkas 56% dengan nisbah daging ke tulang 4.9:1, serta boleh makan semua jenis rumput yang sesuai, menjadikannya pilihan ideal untuk penternak. Kambing BK ialah baka tempatan yang sesuai untuk penternakan, dengan berat matang 48 - 50 kg pada umur dua tahun dan daya tahan tinggi terhadap cacing. Ia mempunyai prestasi pembiakan yang baik (kadar kebuntingan 88.7%, kelahiran 121.4%, dan 42% anak kembar) serta boleh dibiakkan seawal usia 10 bulan. Kambing ini menghasilkan karkas berkualiti tinggi (49 - 51%) dengan nisbah daging ke tulang 3.65:1 dan kurang berbau hamis, menjadikannya pilihan ideal untuk penternak. Ayam Saga merupakan baka ayam kampung asli tempatan yang bersifat dwifungsi bagi pengeluaran daging dan telur dan sesuai diternak di dalam semua jenis sistem pengeluaran. PAKEJ FORMULASI PEMAKANAN TEPAT (PRECISION FEEDING) KATJANG-BOER Teknologi ini dapat membantu penternak mencapai berat optimum ternakan dengan formulasi mengikut peringkat produksi. Teknologi ini berupaya membantu meningkatkan berat badan ternakan sehingga ke 35 – 40%. FORMULASI MAKANAN AYAM BERASASKAN SUMBER TEMPATAN MARDI juga berjaya menghasilkan dua jenis formulasi makanan ayam kampung iaitu berasaskan hampas isirung sawit dikenali sebagai PKfeed dan berasaskan temukut. Penggunaan bahan tempatan ini mampu menggantikan lebih 40% jagung import dan mil kacang soya. Mesin Otosil® berfungsi untuk menghasilkan silaj iaitu sejenis makanan ternakan ruminan yang mengalami proses pemeraman dan dihasilkan dalam bekas kedap udara yang dibuat sama ada plastik atau tong drum. Teknologi ini menyediakan satu platform yang lebih tepat melalui aplikasi teknologi DNA bagi pengenalpastian komposisi baka kambing tulen. Oleh yang demikian, pembangunan baka baharu akan lebih tepat dan berkesan, secara langsung dan mengurangkan kos yang terlibat. Panel penanda SNP boleh digunakan oleh pembaik baka lembu dalam pengenalpastian/pengesahan tahap ketulenan baka atau komposisi darah baka tersebut sebelum memulakan sebarang program pembaikbakaan.
BAKA LEMBU KEDAH-KELANTAN (KK) ELIT


KAMBING KATJANG X BOER (BK)
AYAM KAMPUNG MARDI/AYAM SAGA
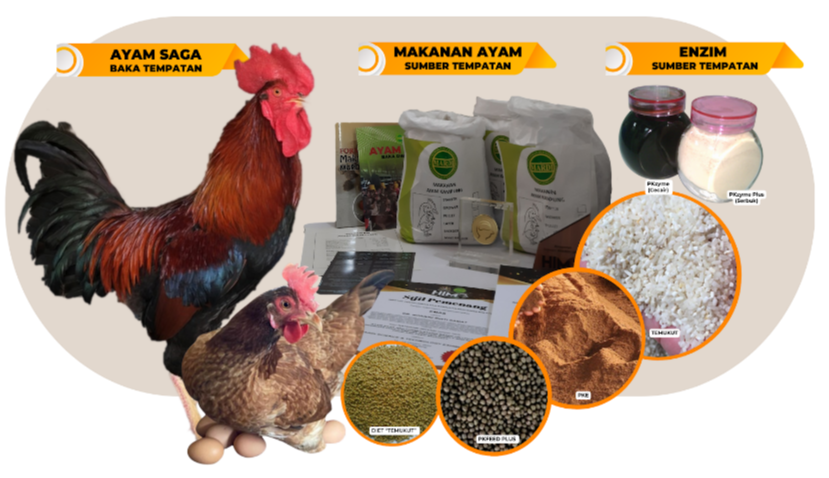




PEMAKANAN TEPAT (KAMBING BK, LEMBU BRAKMAS DAN LEMBU KK ELIT)
Konsep pemakanan tepat adalah pemberian makanan ternakan mengikut keperluan nutrisi bagi meningkatkan tahap produksi dan kualiti baka yang dihasilkan.

MESIN PEMBUATAN SILAJ OTOSIL

PENANDA MOLEKUL SNP BAGI KATJANG TULEN
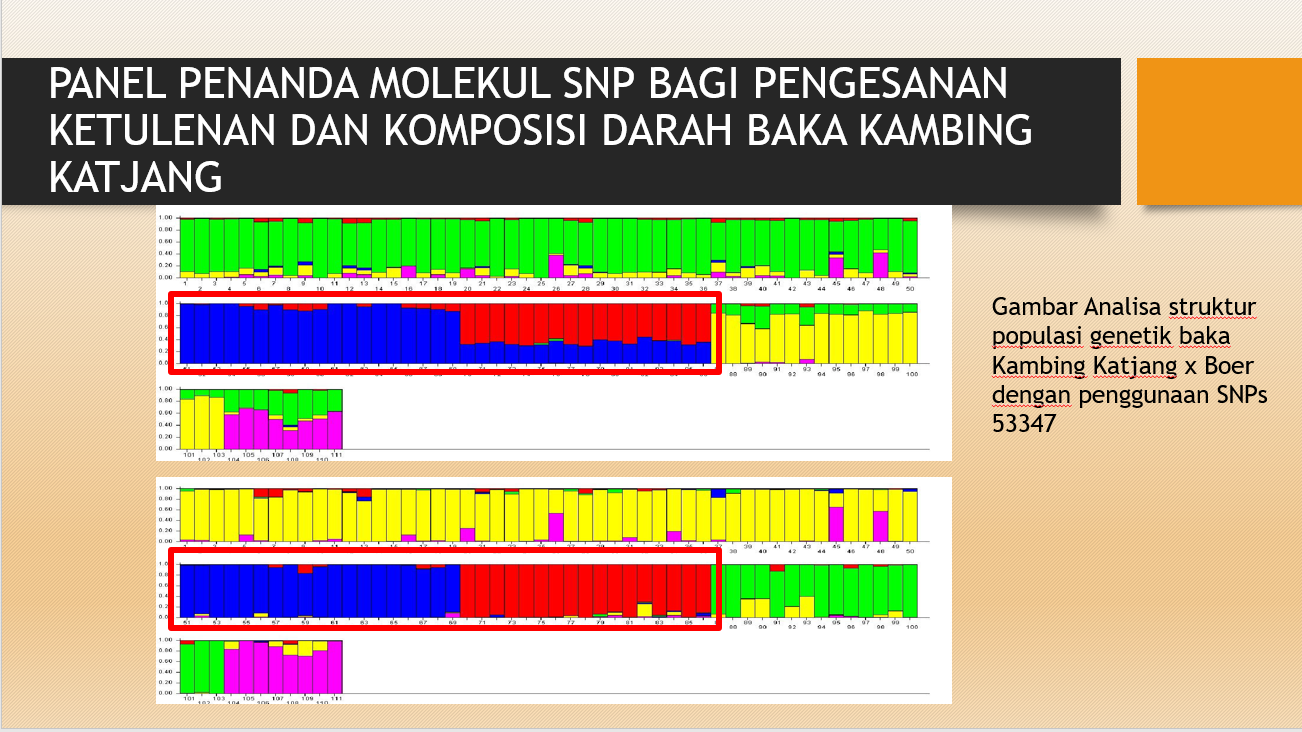

PENANDA MOLEKUL KAMBING KACUKAN KATJANG-BOER
Penanda genetik membantu dalam pemilihan kambing kacukan Katjang-Boer yang mempunyai prestasi pertumbuhan baik di peringkat awal iaitu seawal umur enam bulan dengan lebih tepat.
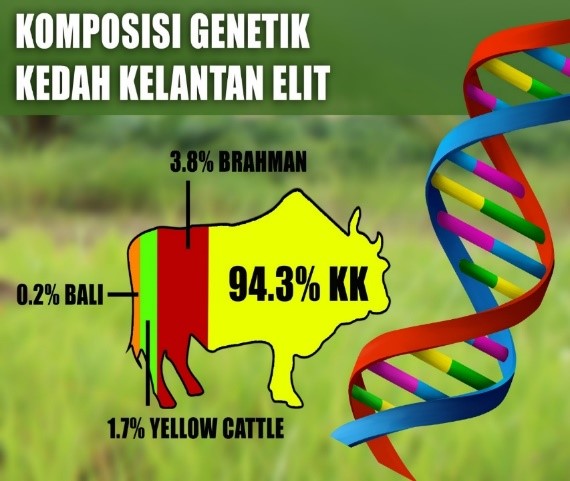
PENANDA MOLEKUL UNTUK BAKA TERPILIH BRAKMAS DAN KEDAH-KELANTAN
Publications
- Abdul Mu'in, H. B., Julie Marzlinda, M. R., and Muhammad Hafizul Rahman, M. A. (2023). Kajian keupayaan reproduktif: kadar volusai pada baka kambing boer dan katjang. Buletin Teknologi MARDI.
- Ainu Husna, M. S. S., Rabiatul Adawiah, Z. A., Fairuz, M. Y., Abdullah, M. R., Abdullah, S., and Khatijah, Y. (2023). In silico analysis of xylanase in Bacillus coagulans ST-6. Asia Pacific Journal of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology 31, 17-27.
- Dzufazly, A., Mohd Rosly, S., Predith, M., Marini, A. M., Nasyatul Ekma, M. H., Darus, A. R., and Siti Masidayu, M. S. (2023). Karakteristik Karkas Baka Lembu Pedaging Teknologi MARDI I - Perbandingan Fizikal. Buletin Teknologi MARDI 36, 135-144.
- Dzufazly, A., Mohd Rosly, S., Predith, M., Marini, A. M., Nasyatul Ekma, M. H., Darus, A. R., Salma, M. Y., Nurul Nuraliya, S., and Siti Masidayu, M. S. (2023). Karakteristik Karkas Baka Lembu Pedaging Teknologi MARDI II - perbandingan karakteristik karkas dan kualiti daging. Buletin Teknologi MARDI 36, 117-124.
- Farah Nurshahida, M. S., Nooraisyah, S., Noraini, S., and Nazikussabah, Z. (2023). Nilai proksimat dan ciri fizikal pelet ayam pedaging ditambah dengan rumpai laut merah dan coklat. Buletin Teknologi MARDI 36.
- Farahiyah Ilyana, J., Mardhati, M., Nurulhayati, A. B., Yong, S. T., Lokman-Hakim, I., and Noraini, S. (2023). The Effect of Canola Oil Supplementation at Different Feeding Duration on Local Chicken, Ayam Saga Growth Performance, Carcass Composition and Omega-3 Fatty Acid Content. Malaysian Journal Animal Science 25, 35-43.
- Mohd Hafiz, A. W., Mohamad Hifzan, R., Izuan Bahtiar, A. J., and Nurulhuda, M. O.(2023). Penganggaran berat badan Kambing Katjang-Boer jantan berdasarkan ukuran badan. Buletin Teknologi MARDI 36, 1-8.
- Nurulhuda, M. O. (2023). Penilaian Rangsum Makanan Lengkap (TMR) Berasaskan Sumber Makanan Tempatan ke atas Biri-Biri Dorper di Peringkat Laktasi. Buletin Teknologi MARDI 36.
- Yong, S. T., Tan, H. Y., Noraini, S., and Wong, H. K. (2023). Penghasilan telur berkolesterol rendah melalui rawatan beras yis merah. Buletin Teknologi MARDI 38, 89-96.
- Mohd Hafiz, A. W., Mohamad Hifzan , R., Izuan Bahtiar, A.J., Mohd Rosly, S. and Marini, A.M. (2022). Corak pertumbuhan lembu Brakmas. Buletin Teknologi MARDI 31, 159-166.
- Mohd Hafiz, A. W., Mohamad Hifzan, R., Izuan Bahtiar, A. J., and Nurulhuda, M. O. (2021). "Evaluation of principal component analysis in animal breeding and selection in the breed improvement program of Male Katjang-Boer Crossbred," Malaysian Journal ofAnimal Science, Vol. 24, No. pp. 33-40.
- Nik Siti Mariani, W. H., Wan Zahari, M., Marini, A. M., Abd Rahman, A., Shanmugavelu,S., and Halimatun, Y. (2021). "Effect of two levels of selenium supplementation on the libido,scrotal circumference, sperm quality and testosterone levels of matured Boer bucks," Tropical Animal Science Journal, Vol. 44, No. 5,.
- Nik Siti Mariani, W. H., Marini, A. M., Wan Zahari, M., Shanmugavelu, S., and Halimatun,Y. (2021). "Effect of two levels of organic selenium supplementation on the nutrient digestibilityof matured Boer bucks," Malaysia Journal of Anmial Science, Vol. 24, No. 1, pp.23-32.
- Predith, M., Mohamad Hifzan, R., and Mohd Azlan, P. (2021). "Evaluation Of Nutritional Needs, Body Weight Gain And Economic Viability Of Stage Feeding On Katjang-Boer CrossbredGoats," Malaysian Journal of Veterinary Science, Vol. 12, No. 1, pp. 21-33.
- Yong, S. T., Tan, H. Y., Noraini, S., and Wong, H. K. (2021). "The effect of high monacolin Kred yeast rice supplement on performance, egg quality, egg yolk cholesterol, plasmalipids and enzyme profile of laying hens," Animal Production Science, Vol. 61, No. 16, pp. 1672-1779.
- Mohd Hafiz, A. W., Mohamad Hifzan, R., Izuan Bahtiar, A. J., and Nurulhuda, M. O. (2020). "Estimation of body weight growth curve parameters of Katjang-Boer crossbred.," MJAS,Vol. 23, No. 2, pp. 40-46.
- Predith, M., Shanmugavelu, S., Mohamad Hifzan, R., and Mohd Hafiz, A. W. (2020). "Pre-weaning growth performance of F1 dan F2 Katjang-Boer crossbreds fed formulated creep feed.," MJAS, Vol. 23, No. 2, pp. 62-71.
- Predith, M., Shanmugavelu, S., Marini, A. M., and Nasyatul Ekma, M. H. (2020). "Evaluation of raw oil palm empty fruit bunch (OPEFB) and OPEFB silage (with or without 5% molasses) as a roughage source in ruminant feed through proximate analysis, in vitro and in saccostudies.," Journal of Tropical Agriculture and Food Science.
- Mohd Hafiz, A. W., Marini, A. M., Mohd Rosly, S., Mohamad Hifzan, R., Izuan Bahtiar, A.J., and Shanmugavelu, S. (2019). "Describing growth pattern of selected Kedah-Kelantan cows using non-linear regression models," Mal.J.Anim.Sci., Vol. 22, No. 1, pp. 47-54.
- Roziatul Erin, A. R., Sarah, R., Norham, I., and Noraini, S., (2019). "Effects of different energy and protein levels on growth performance of MARDI village chicken or Ayam Kampung MARDI (AKM) at breeder phase,"Mal.J.Anim.Sci., pp. 123.
Contact
DIRECTOR,
LIVESTOCK SCIENCE RESEARCH CENTER,
MARDI HEADQUARTERS,
PERSIARAN MARDI-UPM,
43400 SERDANG, SELANGOR
TEL:03-89536660 FAX: 03-89536666
- Published on 10 November 2022
- Last modified on 11 March 2025
 Bahasa Melayu
Bahasa Melayu  English
English 